约束平滑器
基于nav2_smac_planner中原始弃用的平滑器,并由`RoboTech Vision`_使其处于可操作状态的nav2_smoother插件。适用于需要将全局规划路径远离障碍物和/或使用Reeds-Shepp运动模型的应用程序。
重要提示:约束平滑器使用一种相当复杂的优化算法,因此建议在定期截断的路径上使用。可以使用“TruncatePathLocal BT Node”来实现适当的路径长度,并可以使用“DistanceController BT Node”来实现周期性。
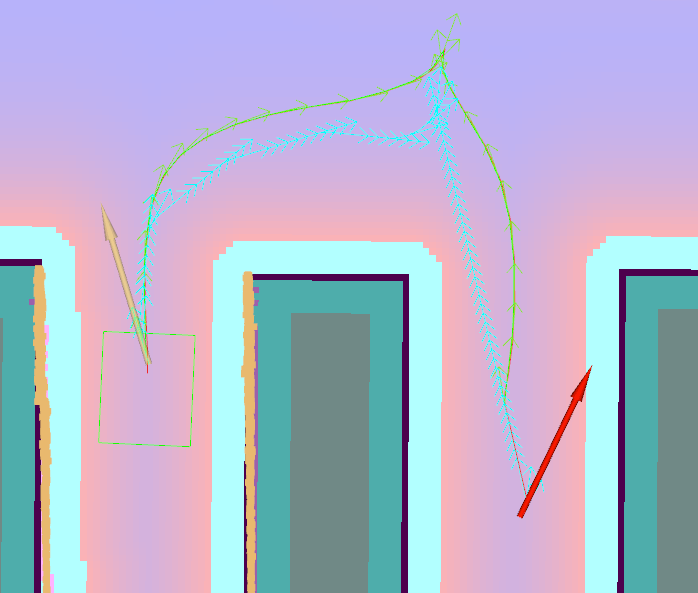
以下图像描述了如何通过使用约束平滑器改善输入路径(青色,由旧版本的Smac Planner生成,意图上未经过优化配置以突出平滑器的优势),增加其平滑度并远离障碍物。生成的路径以绿色标记。注意:由于在此路径上使用了TruncatePathLocal,最后几个路径姿势未进行平滑处理。

平滑器服务器参数
- reversing_enabled
类型
默认
布尔值
true
- 描述
是否检测正向/反向方向和拐点。对于未分配方向的路径,应设置为false。
- path_downsampling_factor
类型
默认
int
1
- 描述
对路径的每第n个节点进行优化。用于加速。
- 路径上采样因子
类型
默认
int
1
- 描述
用于细化的上采样因子。0 - 路径保持下采样(参见“path_downsampling_factor”),1 - 使用三次贝塞尔曲线将路径上采样回原始粒度,2... - 更多的上采样。
- 保持起始方向
类型
默认
布尔值
true
- 描述
是否防止起始方向被平滑处理。
- 保持目标方向
类型
默认
布尔值
true
- 描述
是否防止目标方向被平滑处理。
- 最小转弯半径
类型
默认
双精度
0.4
- 描述
机器人能够执行的最小转弯半径。对于差动驱动/全向运动机器人,可以设置为0.0(或者w_curve可以设置为0.0并产生相同的效果)。
- 曲线权重
类型
默认
双精度
30.0
- 描述
强制最小转弯半径的权重
- w_dist
类型
默认
双精度
0.0
- 描述
将路径与原始路径绑定的权重,作为成本权重的可选替代
- w_smooth
类型
默认
双精度
2000000.0
- 描述
用于最大化路径平滑度的权重
- w_cost
类型
默认
双精度
0.015
- 描述
将机器人远离碰撞和成本的权重
- w_cost_cusp_multiplier
类型
默认
双精度
3.0
- cusp_zone_length
类型
默认
双精度
2.5
- 描述
cusp区域周围的部分长度,在此区域内的节点使用``w_cost_cusp_multiplier``(w_cost在区域内逐渐上升,直至达到拐点,其costmap权重等于w_cost*w_cost_cusp_multiplier)
- cost_check_points
类型
默认
double数组
[]
- optimizer.max_iterations
类型
默认
int
100
- 描述
优化器迭代的最大次数
- optimizer.debug_optimizer
类型
默认
布尔值
false
- 描述
是否打印优化器调试信息
- optimizer.linear_solver_type
类型
默认
string
"SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY"
- 描述
优化器使用的线性求解器类型。有效值为``SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY``和``DENSE_QR``
- optimizer.gradient_tol
类型
默认
布尔值
1e-10
- 描述
梯度容差优化终止条件
- optimizer.fn_tol
类型
默认
布尔值
1e-7
- 描述
函数容差优化终止准则
- optimizer.param_tol
类型
默认
布尔值
1e-15
- 描述
参数容忍度优化终止准则
示例
smoother_server:
ros__parameters:
use_sim_time: True
smoother_plugins: ["SmoothPath"]
SmoothPath:
plugin: "nav2_constrained_smoother/ConstrainedSmoother"
reversing_enabled: true # whether to detect forward/reverse direction and cusps. Should be set to false for paths without orientations assigned
path_downsampling_factor: 3 # every n-th node of the path is taken. Useful for speed-up
path_upsampling_factor: 1 # 0 - path remains downsampled, 1 - path is upsampled back to original granularity using cubic bezier, 2... - more upsampling
keep_start_orientation: true # whether to prevent the start orientation from being smoothed
keep_goal_orientation: true # whether to prevent the gpal orientation from being smoothed
minimum_turning_radius: 0.40 # minimum turning radius the robot can perform. Can be set to 0.0 (or w_curve can be set to 0.0 with the same effect) for diff-drive/holonomic robots
w_curve: 30.0 # weight to enforce minimum_turning_radius
w_dist: 0.0 # weight to bind path to original as optional replacement for cost weight
w_smooth: 2000000.0 # weight to maximize smoothness of path
w_cost: 0.015 # weight to steer robot away from collision and cost
# Parameters used to improve obstacle avoidance near cusps (forward/reverse movement changes)
w_cost_cusp_multiplier: 3.0 # option to use higher weight during forward/reverse direction change which is often accompanied with dangerous rotations
cusp_zone_length: 2.5 # length of the section around cusp in which nodes use w_cost_cusp_multiplier (w_cost rises gradually inside the zone towards the cusp point, whose costmap weight eqals w_cost*w_cost_cusp_multiplier)
# Points in robot frame to grab costmap values from. Format: [x1, y1, weight1, x2, y2, weight2, ...]
# IMPORTANT: Requires much higher number of iterations to actually improve the path. Uncomment only if you really need it (highly elongated/asymmetric robots)
# cost_check_points: [-0.185, 0.0, 1.0]
optimizer:
max_iterations: 70 # max iterations of smoother
debug_optimizer: false # print debug info
gradient_tol: 5e3
fn_tol: 1.0e-15
param_tol: 1.0e-20